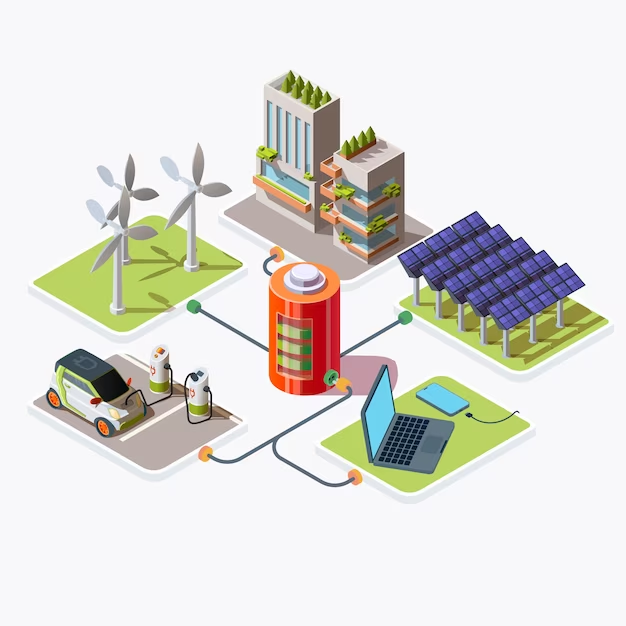
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources like solar and wind, the challenge of inconsistent energy supply becomes more pronounced. This is where energy storage, a critical but often overlooked component of the renewable energy ecosystem, plays a vital role. Effective energy storage systems are essential for stabilizing power grids and ensuring a steady supply of energy, regardless of the intermittent nature of renewables.
The Importance of Energy Storage
Renewable energy sources, while sustainable and environmentally friendly, don’t produce power uniformly. The sun doesn’t always shine, and the wind doesn’t always blow. Energy storage systems address this inconsistency by storing excess energy produced during peak periods and releasing it when production drops, thus balancing supply and demand.

Advancements in Battery Technology
Lithium-ion batteries, known for their use in smartphones and electric vehicles, have become more prevalent in large-scale energy storage. They offer high energy density and long lifecycles, making them suitable for grid storage applications. However, concerns over cost, resource availability, and environmental impact have driven research into alternative chemistries like sodium-ion, solid-state, and flow batteries.
Beyond Batteries: Diverse Storage Solutions
While batteries are the most recognized form of energy storage, other technologies are gaining traction. Pumped hydro storage, which uses excess electricity to pump water uphill to a reservoir, remains the most utilized storage method globally. During periods of high demand, the water is released back downhill to generate electricity.
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) is another promising technology. It involves compressing air during periods of low energy demand and releasing it to turn a turbine when needed. Similarly, flywheel energy storage systems store energy in a rotating mass and release it as rotational energy.
Integration Challenges and Solutions
Integrating energy storage into existing power grids is not without challenges. It requires substantial investment and changes to grid infrastructure. However, advancements in smart grid technology, which use digital communication to detect and react to local changes in usage, are making this integration smoother and more efficient.
Policy support is also crucial. Governments can encourage the adoption of energy storage through incentives and regulatory support, much like they have done for solar and wind energy in recent years.
Conclusion
The future of a renewable-powered world hinges significantly on the advancements and integration of energy storage systems. From battery technologies to alternative storage methods like pumped hydro and CAES, the diversity and innovation in this field are key to managing the variability of renewable energy. As we continue to embrace solar and wind power, energy storage will play an increasingly critical role in ensuring a stable, sustainable, and efficient energy supply for the future.